It’s now been one week since Google Penguin 2.0 went live. Google’s Distinguished Engineer Matt Cutts promised the new generation of Penguin would go deeper, and it seems to have lived up to that promise.
Here are some early findings from sites hit by Penguin.
Does Google Penguin 2.0 Go Deeper on Spammy Links?
Last year after Google Penguin 1.0 launched, Glenn Gabe at G-Squared Interactive did an analysis of sites that lost traffic and rankings, and I covered in “Google Penguin Update: 5 Types of Link Issues Harming Some Affected Websites“. Those link issues were:
- Paid text links using exact match anchor text.
- Comment spam.
- Guest posts on questionable sites.
- Article marketing sites.
- Links from dangerous sites.
Gabe is back with a new Penguin analysis that confirms Google is now looking at more than links to the home page. He examined the content and link profiles of 13 sites that lost traffic and rankings after Google deployed Penguin 2.0 last week.
Once again, heavy usage of exact match anchor text (for so-called “money keywords“) was the biggest culprit. All 13 of the websites Gabe looked at all had heavy use exact match anchor text links aimed at deeper pages (i.e., not just the home page), such as category and subcategory pages:

If you’ve followed Penguin, nothing here should be shocking. Just as Google Penguin targeted unnatural link profiles, so too does Google Penguin 2.0. The big difference now is that Penguin is taking a closer look at more than just the home page.
2 Google Penguin 2.0 Case Studies
Sistrix and Searchmetrics have both put out lists of sites of Penguin 2.0 “losers”. As a general rule, we’ve stopped covering these lists as often the data can be misleading.
That said, Link Research Tools has taken a deep dive into a couple of the Penguin 2.0 casualties mentioned on those lists: HOME24.DE and cheapoair.com. Both saw massive search visibility drops (though it’s not clear whether they have taken an equivalent traffic hit). Both of these excellent case studies are definitely worth a read.
Essentially, both sites scream “spam!” to Google for various reasons, but both had the same issue with “money keywords”. These sites stuck out more than their competitors in a variety of ways in their link profiles – for example, cheapoair.com had “66% Money Keywords while the total average of the other 10 competitors at only 29%.” Also note the lack of “brand” links:
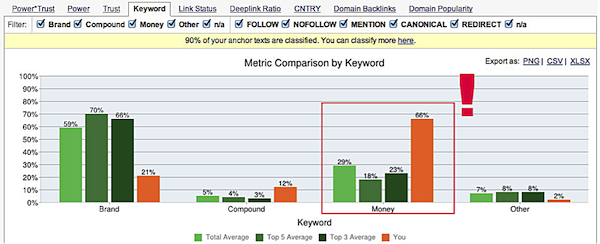
Also problematic are links from sites infected with malware, and pages that are no longer indexed. Christoph Cemper also noted HOME24.DE had an issue with several unhealthy redirected domains, and raises a possible concern:
…penalties were said not to pass via 301 redirects in the past – did that change with Penguin 2.0? 301ing was used for a while to get rid of penalties, and … if that [changed] it would open up a whole new can of worms for negative SEO. Big time.
Summary
While these are early findings, they do offer some confirmation on why sites got hit by Penguin 2.0. Gabe advises working to remove as many unnatural links as you can manually before disavowing the rest.
Cleaning up your profile likely won’t be enough to recover from Penguin 2.0, however. This isn’t a manual penalty, it’s an algorithmic update. Still, there are some steps you can take to beef up your link profile and start showing Google stronger brand signals.

